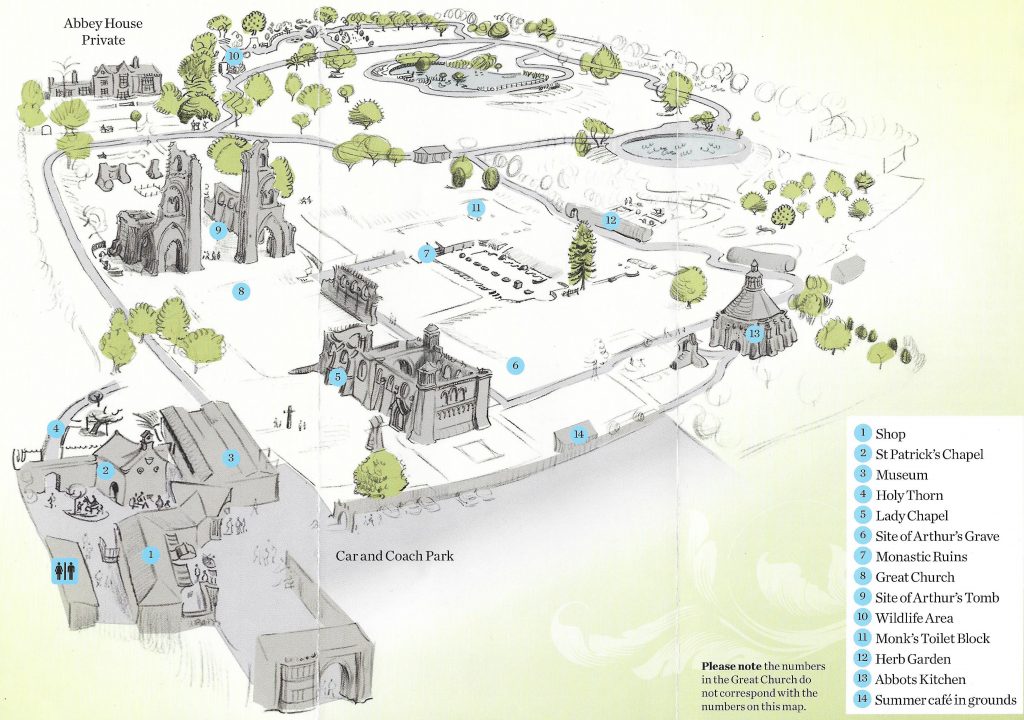
Glastonbury in 1397 is the setting for Joseph of Arimathea’s Treasure, the fifth novel in my Lady Apollonia West Country Mystery Series. The medieval history of the town of Glastonbury was intimately tied to Glastonbury Abbey, and the town had built up around the abbey grounds. With one exception, all the abbey buildings within the abbey grounds are gone or in ruins. I have discussed them in my previous posting.
Glastonbury in 1397 is the setting for Joseph of Arimathea’s Treasure, the fifth novel in my Lady Apollonia West Country Mystery Series. The medieval history of the town of Glastonbury was intimately tied to Glastonbury Abbey, and the town had built up around the abbey grounds. With one exception, all the abbey buildings within the abbey grounds are gone or in ruins. I have discussed them in my previous posting.
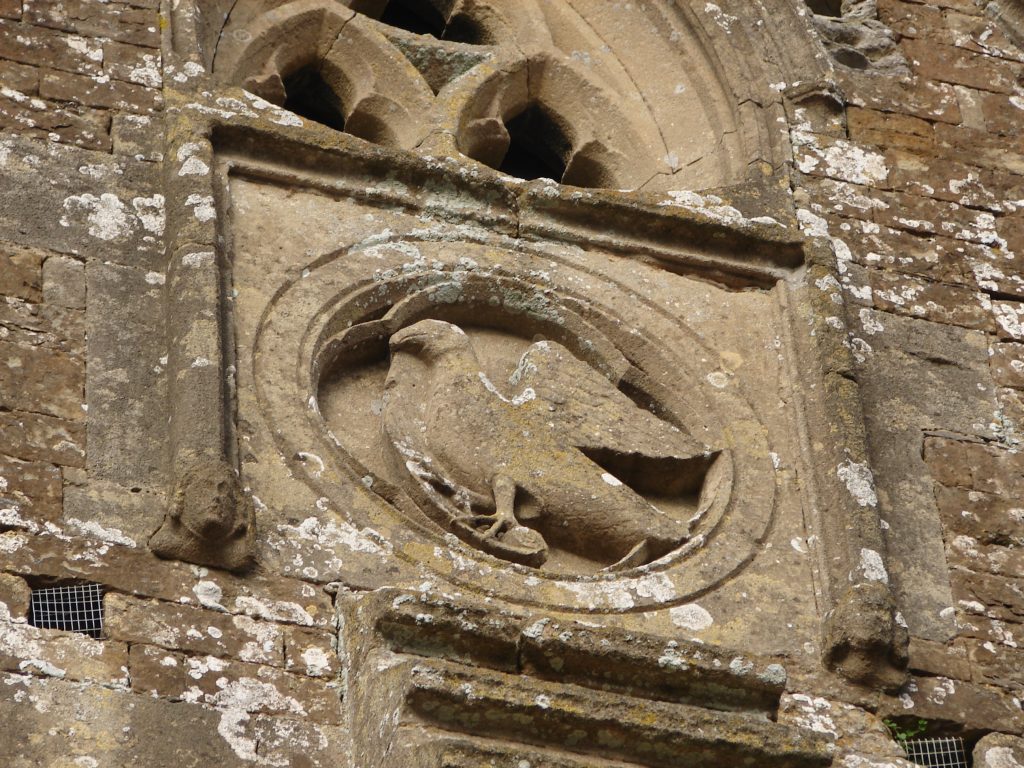
There are abbey buildings, however, which survive in the town and elsewhere. Some are just outside the perimeter of the abbey grounds and they play a role in my story. Beyond the southeast corner of the grounds is the abbey tithe barn, still in excellent condition and housing the Somerset Rural Life Museum. It is cruciform in shape like a church with symbols of the four evangelists carved on the four gable ends. The picture above shows the eagle of Saint John the Evangelist on the west side of the building. This tithe barn also plays a role in my story.
The George Hotel and Pilgrim’s Inn on the High Street in Glastonbury was the abbey inn for pilgrims by the 15th century, but the abbey’s interest in encouraging pilgrimage goes back to earlier centuries. I have described in my story that the pardoner, Bryan Landow was able to obtain accommodation the abbey’s Pilgrim Inn.
The local churches in Glastonbury were controlled by the abbey. Two of them remain today. Saint John the Baptist is on the High Street and plays a major role in my story. My husband and I worshipped there on a couple of Sunday mornings when we were doing research for my book. Saint Benedict, the other existing medieval church, stands to the west of the abbey grounds and is perfectly in line with the location of the abbey church.
Three other abbey buildings still exist in the village of Meare, just a few miles outside Glastonbury in the Somerset Levels. The most important to my story is the Abbot’s Fish House, the only surviving monastic fishery in England. It is a rectangular stone building which was constructed for the storage and processing of fish with a residence on the upper floor for the chief fisherman.
The Church of Saint Mary and the abbot’s summer residence are two other buildings associated with Glastonbury Abbey which still exist in Meare. The abbot’s residence is now a grand farmhouse, but the church is now affiliated with the churches of Saint John the Baptist and Saint Benedictine Glastonbury, which I mentioned earlier, into one parish of the Church of England.
For more on the abbey tithe ban, click on
http://www.greatbarns.org.uk/glastonbury_abbey_barn.html or on
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Somerset_Rural_Life_Museum .